The What-If analysis technique is a brainstorming approach conducted by a group of experienced person and familiar with the subject process. However, What-If Analysis is not as inherently structured as HAZOP Analysis and FMEA analysis.
The What-If analysis technique is the same as the HAZOP technique which allows experts to use their experience more creatively. Both technique offers a different way for the question to be focused. The HAZOP used “HAZOP guidewords” such as “No”, “More”, etc mix with process parameters “Flow”, Temperature”, etc. This is called “Process Deviation”. But What-If techniques use “What-If” to question the participant.
This technique is creatively processed and it is more likely to uncover unique or unexpected hazards in processes. However, unless the team leader is highly skilled and the team members have appropriate experience, critical and important hazards may be overlooked.
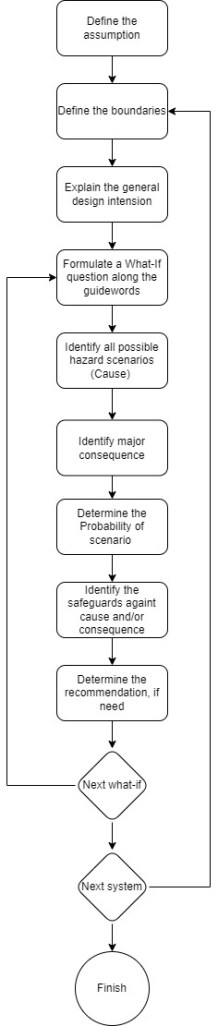
What-If Analysis Workflow
Below is the What-If Analysis working flowchart.
Example of What-If Worksheet
| What If | Hazard | Consequence | Safeguards | Recommendation |
| Piping leakage | Potential of fire, if ignited, and asset damages. | Potential of fire, if ignited and asset damages. | Hazard Area Classification, Gas Detector | |
| Blockage of suction strainer | Loss of liquid flow through the pump | The potential of pump cavitation and damages | Differential pressure across the suction strainer | |
| Pump trips | Loss of liquid flow supply to the column | The potential cause of low liquid level in the column | The standby pump |
Challenges of What-If Analysis
Assumption Dependency: Results from What-If analysis heavily depend on the accuracy of the assumptions and input values. If these assumptions are flawed, the analysis may provide misleading results.
Complexity: In some cases, the models used for What-If analysis can be complex. requiring specialized knowledge and expertise to develop and interpret the results.
Limited Prediction: While What-If analysis is useful for exploring potential outcomes, it may not provide precise predictions, especially in complex and dynamic environments.
Overlook Unforeseen Factors: What-If analysis is based on known variables and assumptions. It may not account for unforeseen factors or external events that could significantly impact the outcomes.