บทความนี้จะพูดถึงวิธีการหาระดับของความปลอดภัย หรือ Safety Integrated Level (SIL) ที่ต้องการ ที่เรียกว่า SIL Determination Study หรือ SIL Classification Study จาก international standard เช่น IEC 61508-5 – Functional Safety of Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Electronic Safety-Related System Part5: Examples of Methods for the determination of safety integrity levels และ IEC 61511-3 – Functional Safety – Safety instrumented Systems for the process industry sector – Part 3: Guidance for determination of the required safety integrity levels
Risk Graph Method
วิธีแรกนี้ชื่อว่า วิธีใช้กราฟความเสี่ยง หรือ Risk Graph หรือ Risk Matrix โดยอาศัยหลักการประเมินความเสี่ยงผ่านแผนภูมิต่างๆ ทั้งที่เป็น แผนภูมิความเสี่ยงที่เกี่ยวกับตัวบุคคล Personal Safety เกี่ยวกับสิ่งแวดล้อม Environmental เกี่ยวกับเครื่องจักร Asset
โดยการใช้แผนภูมิจะมีการนำตัวแปรต่างๆมาใช้งาน เช่น ความรุนแรง (C = Consequence) ความเป็นไปได้ที่จะสัมผัสความอันตราย (F = Frequency of exposure) ความเป็นไปได้ในการหลบหนี (P = Potential of avoidance) และความถี่ในการเกิดเหตุการณ์ (W = Hazard demand rate)
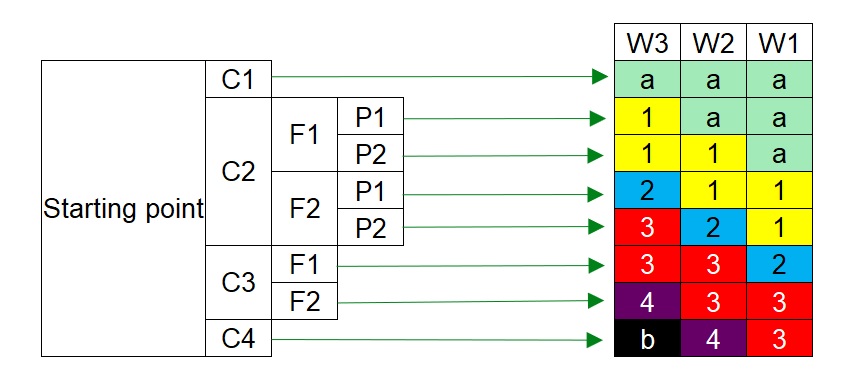
โดยตัวอย่างเกณฑ์การเลือกใช้ค่า Consequence Severity (C), Frequency of exposure (F), Potential of avoidance (P), และ Hazard Demand Rate (D) สามารถเลือกได้จากตารางข้างล่าง
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Consequence Severity (C) | Minor injury | Single fatality | 1-3 Fatalities | > 3 Fatalities |
| Frequency of exposure (F) | < 2 hr/day | > 2 hr/day | ||
| Potential of avoidance (P) | Possible | Difficult | ||
| Hazard Demand Rate (D) | < 1 year | 1-10 year | > 10 years |
หลังจากเลือกใช้ค่าต่างๆตามตารางแล้ว สามารถได้ระดับ SIL ไม่ว่าจะเป็น SIL-a, SIL-1, SIL-2, SIL-3, SIL-4, และ SIL-b
โดยที่ SIL-a มีความหมายว่า gap ของความเสี่ยงนั้น ไม่ได้สูงมากสามารถจัดการได้ด้วยระบบอื่นที่ไม่ใช่ระบบ Safety Instrumented System (SIS) เช่น ระบบ Basic Process Control System (BPCS)
และ SIL-b มีความหมายว่า gap ของความเสี่ยงนั้นมีความสูงมากๆ ไม่สามารถจัดการได้ด้วยระบบ Safety Instrumented System (SIS) เพียงระบบเดียว จำเป็นต้องมีระบบอื่นเข้ามาช่วย เช่น ระบบเครื่องกล Mechanical Device เช่น PSV เป็นต้น
ทั้งนี้ Risk Graph ของสิ่งแวดล้อม Environment และเครื่องจักร Asset จะมีความแตกต่างจาก Risk Graph ในรูป เพราะตัวแปรบางตัวจะไม่สามารถนำมาพิจารณาได้ เช่น Frequency of exposure (F), และ Potential of avoidance (P) เพราะสิ่งแวดล้อมและเครื่องจักรไม่สามารถหลบหนีจากอันตรายได้ และก็อยู่กับที่ตลอดเวลา
Layer Of Protection Analysis (LOPA) Method
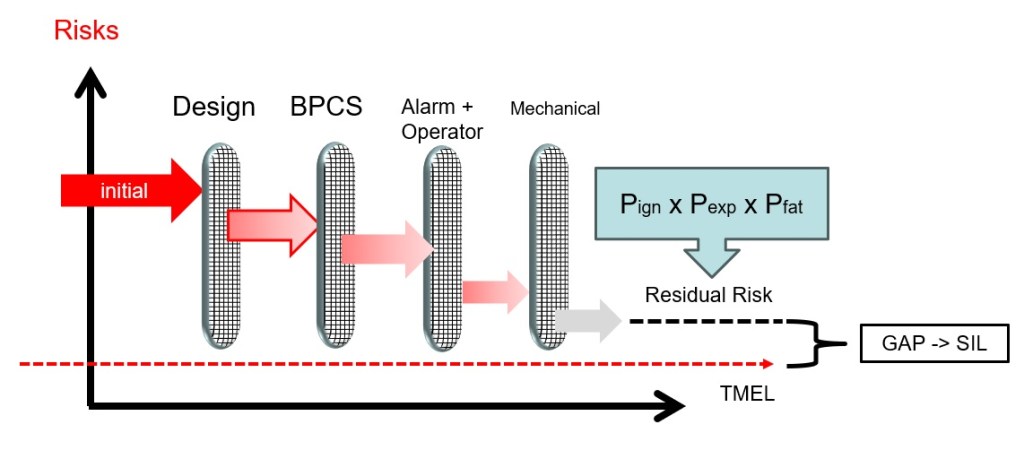
การวิเคราะห์ชั้นการป้องกัน หรือ Layer Of Protection Analysis (LOPA) เป็นอีกวิธีหนึ่งในการกำหนดระดับ SIL โดยการวิเคราะห์ว่าชั้นการป้องกันที่มีอยู่ หรือที่เรียกว่า Independent Layer Of Protection (IPL) ภายในระบบนั้นว่ามีเพียงพอที่จะลดความเสี่ยงของอันตรายให้ถึงระดับที่ยอมรับได้ หรือที่เรียกว่า Target Mitigated Event Likelihood (TMEL) หรือไม่
ผู้ใช้ที่ต้องการใช้วิธีการศึกษา Layer Of Protection Analysis (LOPA) ในการกำหนดระดับ SIL จำเป็นต้องมีความรู้เพิ่มเติมในวิชาคณิตศาสตร์ที่เกี่ยวกับความน่าจะเป็น ซึ่งนี่เป็นความจริงอย่างยิ่ง ที่ว่าไม่มีการป้องกันใดๆ ก็ตามที่จะสมบูรณ์แบบ 100% ยังไงก็มีความเป็นไปได้ที่จะล้มเหลวเมื่อมีความต้องการใช้งานอยู่ และนั่นคือประเด็นหลักของการศึกษา LOPA
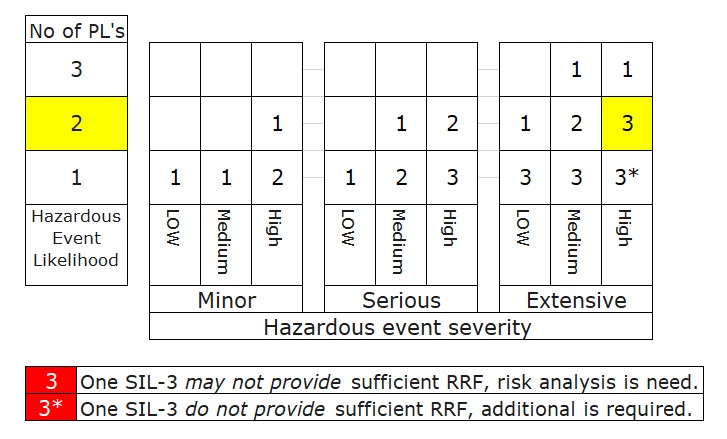
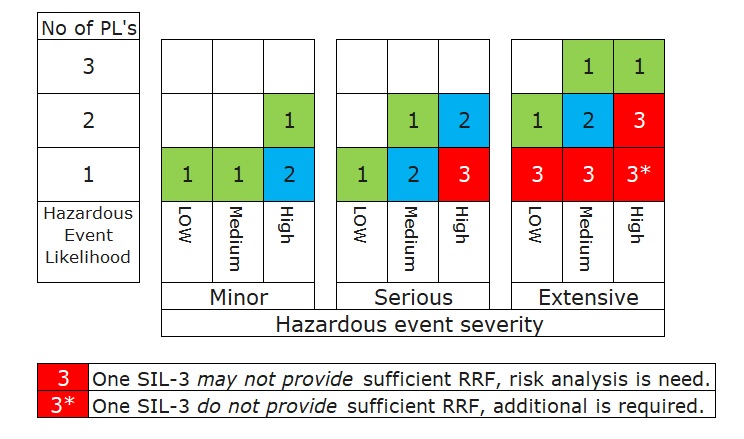
Hazardous Event Severity Matrix or Safety Layer Matrix (SLM)
Same idea with the risk matrix, there is the other method to determine the SIL target by considering the available of the existing of protection layers which uses the qualitative way to identify the SIL target called Safety Layer Matrix (SLM).
Safety Layer Matrix (SLM) มีแนวคิดเดียวกันกับ Risk Matrix Method แต่ก็เป็นอีกวิธีหนึ่งในการกำหนดเป้าหมาย SIL โดยพิจารณาจากความพร้อมของชั้นป้องกันที่มีอยู่ ซึ่งใช้วิธีเชิงคุณภาพในการระบุเป้าหมาย SIL ตามตาราง Matrix ข้างล่าง
Results comparison
ตารางข้างล่างเป็นผลลัพท์การเปรียบเทียบหาระดับการป้องกันอันตราย Safety Integrity Level (SIL) ที่ต้องการ โดยใช้เทคนิค Risk Graph, Safety Layer Matrix, และก็ LOPA
| Risk Graph | SLM | LOPA | |
| Study characteristics | Qualitative | Qualitative | Semi-Quantitative |
| Main Focus | Finding the SILtarget | Finding the SILtarget | Ensure the risk is within tolerable level |
| Component (Human) | – Demand rate – Consequence Level – Prob. of exposure – Prob. of avoidance | – Number of Protection Later | – Demand rate or initiating frequency – Severity Level and TMEL – Ignition Probability – Potential of fatality – Prob. of exposure – PFD of IPL |
| Outcome | SIL level: a,1,2,3,4, or b | SIL level: a,1,2,3,4, or b | SIL Level, PFD, and RRF |
| Time consume | Less | Less | More |
| Conservative | More | More | Less |
| Note | Excludes the existence of the protection. | Excludes the precise value such as Pign, etc | PFD value is subjective. |
Example
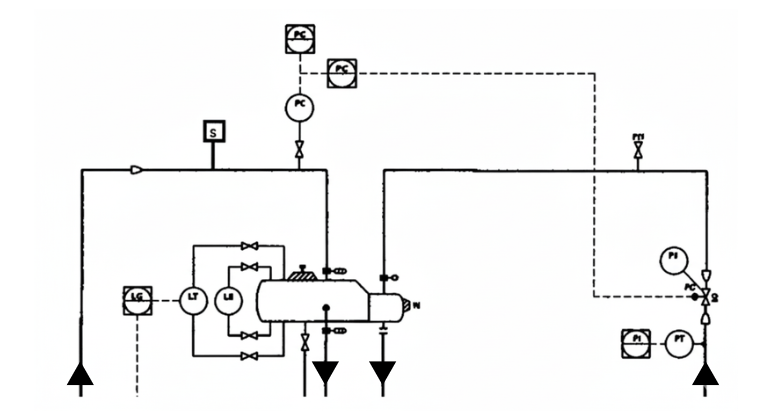
The ethylene evaporator is being considered for the additional Safety Instrumented Function to prevent overpressure scenarios. One potential cause of Loss Of Primary Containment (LOPC) is pressure control malfunction and wide opening of the pressure control valve (PV). This will lead to more of the HP steam supply to the Ethylene Evaporator, and potential of over temperature and over pressure in ethylene evaporator.
- The frequency of failure (BPCS failure) is 1 in 10 year
- IPL is a Pressure Safety Valve (PSV) which can be considered as 2 credits of risk reduction. (PFD is 1E-2 per year)
- The severity level is C4 since the Ethylene will be released to the working area and fire if ignited and based on the company, the TMEL is 1E-6 per year.
- The frequency of the operator accessing the location is approximately 15 mins/shift.
- The probability of ignition of ethylene is 0.3
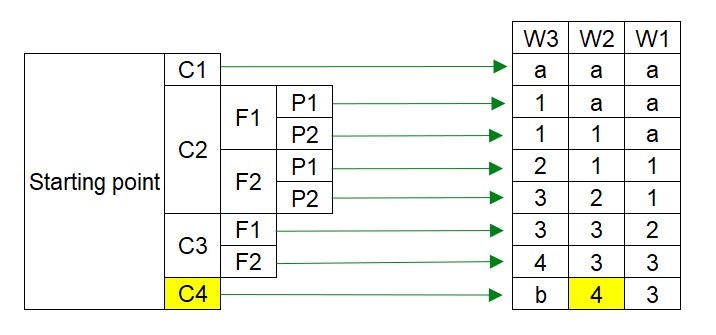
The result of the Risk Graph method is shown as SIL-4 is required. Since the maximum SIL level of process production is limited to the SIL-3 level, then an additional safeguard is required.
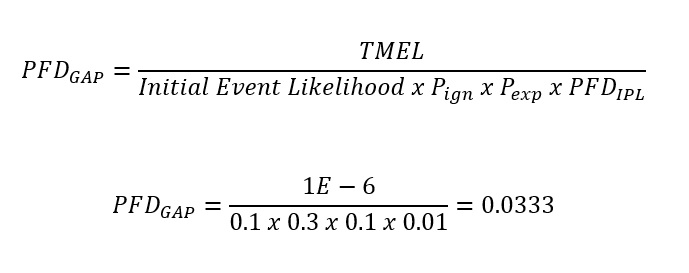
The result of the LOPA method is shown as SIL-1 is required. (RRF = 30.03)
The result of the Safety Matrix Layer (SLM) is shown as SIL-3 is required.