As you know the Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) is a structural and systematic examination of the complex process or system to identify and evaluate potential hazards and operability issues. It is commonly used in industries such as chemical, petrochemical, and nuclear process.
HAZOP can be applied to both continuous and batch processes, but there are some differences in how the studies are conducted to the nature of these processes. Below is the comparison between the continuous process and the batch Process.
| Subject | Continuous | Batch |
| Process Dynamics | The process operates continuously without interruption, The study focuses on the deviations from the normal operating. | The process operates in a series of steps with intermittent periods of production. |
| Mode | Normal, Start-up, and Shutdown | Multiple phases/steps |
| Transient condition | Limit to only start-up, shutdown, and online mode change | Always study the transient |
| Flexibility and Variability | Limit to only some activities such as chemical loading | More flexibility, especially Time-related guidewords |
| Time consideration | Limit only 2 dimensions are (NO/LESS) and Extend (MORE). | Many dimensions of Time-related deviation |
From the above table, the main difference between the batch process and the continuous process is the process dynamics. The batch process will be discussed repeatedly in a series of steps. Hence, the workshop can become worse (discussion back and forth across the worksheet) if not well prepared.
Time-Related Guidewords of the Batch Operation
Below is an example of time-related guidewords that can be applied during the workshop, if relevant. However, it obviously be noticed those guidewords become more relevant when encompassed with human factors.
| Guideword | Interpretation |
| Early/before | something errors and do something earlier than required. |
| Late/after | something errors and do something later than required. |
| Quicker | something errors and do something quicker than required. |
| Slower | something errors and do something slower than required. |
| Repeated | something errors and do something double. |
Example
Below is an example of the Process Flow Diagram (PFD) of the Carbon Filter and Cation Filter in the Demineralized Water Package.
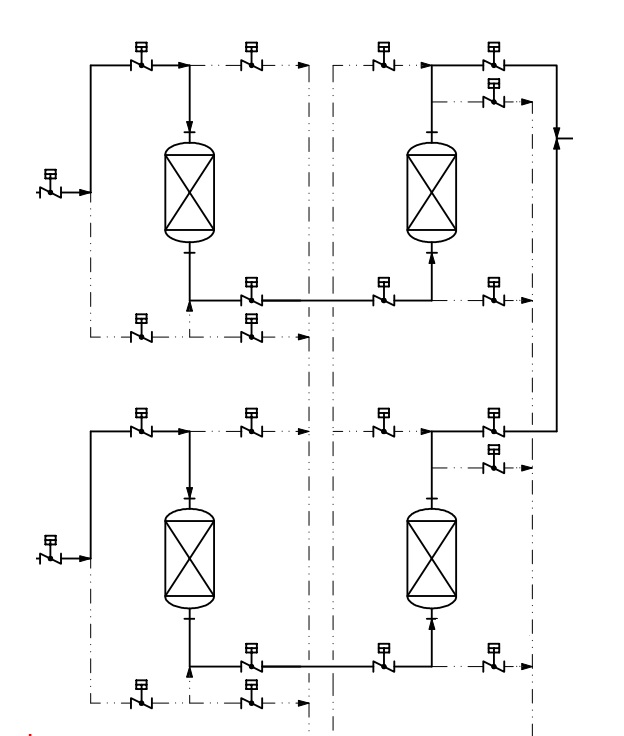
| Stage | Description | Service Inlet | Service Outlet | Backwash Inlet | Backwash Outlet | Rinse Outlet | Vent |
| 1 | Venting | – | – | – | – | – | O |
| 2 | Filling | O | – | – | – | – | – |
| 3 | Pre-Service Rinse | O | – | – | – | O | – |
| 4 | Service | O | O | – | – | – | |
| 5 | Back Wash | – | – | O | O | – | – |
| 6 | Final Rinse and Drain | O | – | – | – | O | O |
The HAZOP worksheet will look like this.
| Deviation | Cause |
| No/Less Flow | Failure and stuck closing of vent valve during the venting stage. |
| Failure and stuck closing of the serive inlet valve during Pre-Service Rinse | |
| Failure and stuck closing of the service inlet valve during Rinse Outlet |
The other way around is using the Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) study for 2 modes either open or closed failure mode during a review against all working steps.
| Failure Mode | Sequence | Consequnce |
| Fail Close of Service Inlet | Venting | No safety issues as the system will understand it as a normal condition. |
| Filling | Leading to No/Less flow of liquid supply to… | |
| Pre-Service Rinse | Leading to No/Less flow of liquid supply to… | |
| Service | Leading to No/Less flow of liquid supply to… | |
| Back Wash | No safety issues as the system will understand it as a normal condition. | |
| Final Rinse and Drain | Leading to No/Less flow of liquid supply to… |
In this way, all valves will be reviewed against all operation modes.